Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a type of pinched nerve in the wrist. It is the most common compression neuropathy in the upper extremity. It results from increased pressure on the median nerve at the wrist, within the carpal tunnel. Symptoms such as numbness, tingling, weakness, and pain can result if the nerve is compressed or “pinched.” Numbness in the hand is often worse at night!
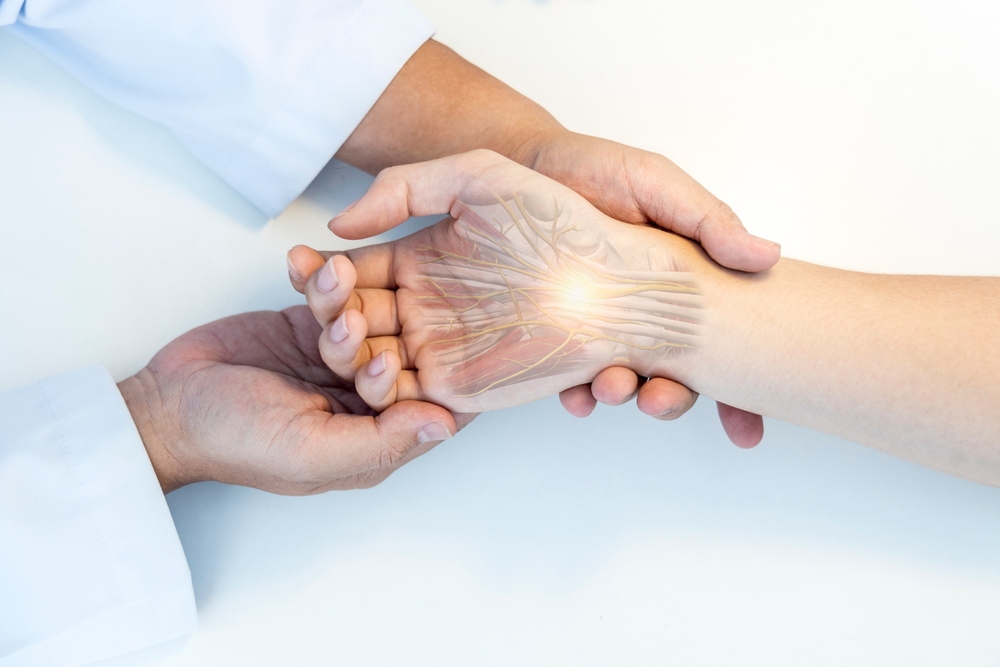
The word “carpus” is derived from the Greek word karpos, which means “wrist.” The carpal tunnel is a passageway in the wrist through which the median nerve and tendons of the hand travel. The carpal tunnel is a narrow, confined space: the floor of the tunnel is made up by the carpal bones of the wrist, and the roof is created by the transverse carpal ligament. The median nerve is at risk for compression within this tunnel. If there is abnormal swelling, altered wrist anatomy, or injury to this area, the function of the median nerve may be affected.
What Causes Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
In most cases, the cause of CTS is unknown. Thyroid disorders, rheumatoid arthritis, pregnancy, vitamin deficiencies, diabetes, fluid retention, and trauma can be associated with CTS. Women are more commonly affected than men. Repetitive, forceful gripping and heavy use of vibratory tools may increase a person’s risk of CTS.
How Do I Know if I Have Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
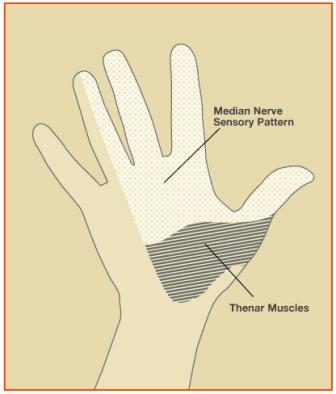
Patients with CTS commonly report “numbness” or “tingling” in the fingers. Some patients feel that the fingertips are “asleep” or report “poor circulation” in the hands. Symptoms are often worse at night and people tend to shake their hands for relief. Some patients report increased symptoms while gripping a steering wheel. Dropping objects, clumsiness with the hands, or a weak grip are also common complaints. Some people also report pain in the forearm, wrist or fingers. In severe cases, the muscles at the base of the thumb (thenar muscles) can become weak and atrophy, sometimes permanently. See image below.
Often the diagnosis can be made on the basis of your symptoms, medical history, and physical examination. An electrodiagnostic study (nerve conduction study and/or electromyogram) can be ordered to confirm the diagnosis.
What Are the Treatment Options for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
Not everyone with carpal tunnel syndrome needs surgery. Fortunately, many people with CTS improve with non-operative treatment. Wearing a wrist brace at night supports the wrist in neutral alignment and takes pressure off the median nerve. Avoiding prolonged wrist flexion and forceful or repetitive gripping may also help. Corticosteroid injections provide an anti-inflammatory effect and can be effective in many patients.
Should these measures fail to improve the condition, or if nerve compression is severe, surgery may be recommended. A carpal tunnel release (CTR) is performed to decrease pressure on the median nerve. During this procedure, the “roof” of the carpal tunnel (the transverse carpal ligament) is divided. Cutting the transverse carpal ligament increases the size of the carpal tunnel and provides more room for the median nerve.
The length and type of incision varies among surgeons; however, the common goal is to reduce pressure on the median nerve. The length of incision used for CTR has decreased in size since the procedure was invented decades ago due to advancements in surgical techniques. Carpal tunnel release surgery can be performed using smaller incisions these days. Open CTR and endoscopic CTR are two surgical options. The recommended procedure will be discussed with you with your doctor.
What is the Recovery Process for Carpel Tunnel Syndrome?
The surgery is performed as an outpatient under local anesthesia. Oral or intravenous (IV) sedation medication may also be used. Patients may use their hands for light activities soon after the surgery. Many people can return to light duty work in a few days. Patients should avoid heavy use of the hand for approximately 3-4 weeks after surgery. As the pain from surgery subsides, normal use of the hand is resumed.
What Are the Expected Results of Carpal Tunnel Surgery?
Most patients are very satisfied with their outcome after CTR surgery. Many patients report rapid improvement in their painful tingling symptoms in just a few days, but other patients may take longer to improve. Some patients do not have complete relief of numbness symptoms, especially in severe or long-standing cases. Temporary soreness or tenderness in the palm can occur with surgery. There is less than 5% recurrence rate after carpal tunnel release surgery.
What Complications Can Arise from Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Surgery?
Complications from carpal tunnel release surgery are uncommon. Possible complications include persistent symptoms, pain, infection, stiffness, and rarely damage to the median nerve.
Take Control of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Today
Are you tired of the tingling, numbness, and pain in your hands? Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (CTS) can be a major problem, but you don’t have to suffer in silence. Our expert team of orthopedic surgeons at Raleigh Hand to Shoulder Center in Raleigh, NC is here to provide you with the latest treatments and solutions to relieve your Carpal Tunnel Syndrome symptoms.
Don’t let Carpel Tunnel Syndrome hold you back from living your life to the fullest. Seek treatment today by filling out the form on the right-hand side of this page. You can also give us a call directly using the phone call button and schedule an appointment button, both located at the top of this page.
Images and video provided by the American Society for Surgery of the Hand. The material provided is intended for general information only and does not constitute medical advice. Use of this site does not replace direct evaluation by a physician.


