Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a type of pinched nerve in the wrist. It is the most common compression neuropathy in the hand and arm. It results from increased pressure on the median nerve at the wrist, within the carpal tunnel. Symptoms such as numbness, tingling, weakness, and pain can result if the nerve is compressed or “pinched.”
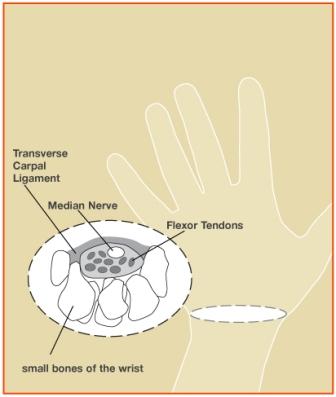
The word “carpus” is derived from the Greek word karpos, which means “wrist.” The carpal tunnel is a passageway in the wrist which contain the median nerve and flexor tendons. The carpal tunnel is a narrow space made up by the bones of the wrist and the transverse carpal ligament. The median nerve is at risk for compression within this tunnel. If there is swelling, abnormal wrist anatomy, or injury to this area, the function of the median nerve may be affected.
WHAT CAUSES CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME?
In most cases, the cause of CTS is unknown. Thyroid disorders, rheumatoid arthritis, pregnancy, vitamin deficiencies, diabetes, fluid retention, and trauma can be associated with CTS. Women are more commonly affected than men. Repetitive, forceful gripping and heavy use of vibratory tools may increase a person’s risk of CTS.
HOW DO I KNOW IF I HAVE CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME?
Patients with CTS commonly report “numbness” or “tingling” symptoms in the fingers. Some patients feel that the fingertips are “asleep” or report “poor circulation” in the hands. Symptoms are often worse at night and people tend to shake their hands for relief to wake them up. Some patients report increased symptoms while gripping a steering wheel. Dropping objects, clumsiness with the hands, or a weak grip are also common complaints. Some people also report pain in the forearm, wrist or fingers. In severe cases, the muscles at the base of the thumb can become weak and atrophy, sometimes permanently.
Often the diagnosis can be made on the basis of your symptoms, medical history, and physical examination. An electrodiagnostic study or nerve test can confirm the diagnosis in some cases.
WHAT ARE THE TREATMENT OPTIONS FOR CARPAL TUNNEL SYNDROME?
Not everyone with carpal tunnel syndrome needs surgery. Many people with CTS improve without surgery. Wearing a wrist brace at night supports the wrist and takes pressure off the median nerve. Avoiding prolonged wrist flexion and forceful gripping may also help. Corticosteroid injections provide an anti-inflammatory effect and can be effective in many patients.
Treatment can include wrist brace, hand therapy, steroid injection and surgery if conservative treatment is not successful. Surgery is usually recommended if there are signs of severe carpal tunnel syndrome or nerve damage. Treatment for carpal tunnel syndrome can alleviate numbness and tingling in the hand at night and improve hand function during the day.
Should these measures fail to improve the condition, or if nerve compression is severe, surgery may be recommended. A carpal tunnel release surgery is performed to decrease pressure on the median nerve. During this procedure the transverse carpal ligament is divided to take pressure off the nerve. Cutting this ligament increases the size of the carpal tunnel and provides more room for the median nerve. The ligament grows back over time, but the tunnel size has been increased.

Raleigh Hand to Shoulder Center doctors are experts in treatment of CTS. They are members of the American Society for Surgery of the Hand. The doctors are board certified by the American Board of Orthopedic Surgery.


